What is LEED?

For those just learning about green building, you’ve come to the right place. We’ve been working on green buildings for years and one of the biggest changes in construction in the last 20 years is the creation of the USGBC and the LEED Rating System. LEED is a rating system that was developed to streamline the process of creating environmentally friendly buildings. LEED looks to reduce energy and water use, create better indoor air quality and environment for occupants and reduce the carbon footprint of the materials used and waste created in the process of construction. Today, there are many different rating systems, but the USGBC and LEED began a movement that propelled the construction industry into going “green”.
LEED itself stands for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design. LEED was created by the USGBC (United States Green Building Council) in 1993 in order to push the building industry in a more environmentally friendly direction. As the construction industry had pretty much operated status quo for almost a century, it was certainly time for a change, and LEED looked to transform the market. According to the EIA, about 40% of all energy consumed in the US in 2015 was from residential and commercial buildings, indicating we can make great reductions in energy demand through better design, smarter construction and more thoughtful renovations of new and existing building stock.
The US currently has around 50,000 LEED projects with another few thousand internationally. While many building projects still operate much like they did fifty years ago, the industry has begun the movement towards more environmentally thoughtful design. Much of LEED’s success can be attributed to its holistic approach to building. Although many experts would agree that energy reduction is the most important focus in sustainable building, it is not the sole focus of LEED, but absolutely a major component.
The holistic approach to green building can be seen over the eight major sections to the LEED program:
- Location & Transportation
- Sustainable Sites
- Water Efficiency
- Energy & Atmosphere
- Materials & Resources
- Indoor Environmental Quality
- Innovation
- Regional Priority
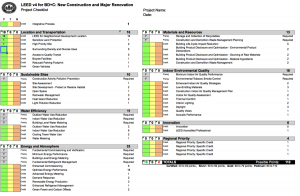
Most of the credit categories are made up of a mixture of prerequisites and credits. Prerequisites are mandatory and all LEED projects must meet these requirements in order to achieve even basic certification. Based on the number of credits achieved, a project is then able to bank points towards earning a level of certification: 40-49 points (Certified), 50-59 points (Silver), 60-79 points (Gold), and 80-110 points (Platinum).
LEED projects look at not just the completed building’s energy and water use, but also the construction process, including waste reduction, habitat restoration, low/no chemical materials (Low VOC and NAUF), and sustainably sourced and manufactured materials (through the use of EPDs – Environmental Product Declaration) Because of the holistic approach, some may find LEED to seem overwhelming and overly complicated, however with a little education (you can earn your LEED AP credential) and some experience on a project, you will have a strong understanding of the program and will be able lead your team on the next LEED construction project and add to the growing number of building projects that are seeing the value in building more sustainably.



